
Cyclone efficiency : step by step shortcut calculation
How to calculate the efficiency of a cyclone ?
Follow us on Twitter ![]()
Question, remark ? Contact us at admin@powderprocess.net
| Section summary |
|---|
| 1. Efficiency of a
cyclone |
| 2. Calculation of
the efficiency of a cyclone : step by step calculation |
| 3. Example of
cyclone efficiency estimation |
| 4. Free Excel calculation tool for estimating a cyclone efficiency |
Cyclones are designed to separate the solids particles from a flow of gas. Cyclones are however not perfect and usually cannot capture all the dust present in a given gas. The capacity of a cyclone to catch the particles in a given gas is called the efficiency of the cyclone. This page present a shortcut calculation to estimate the efficiency of a cyclone.
1. Efficiency of a cyclone
What is the efficiency of a cyclone ?
The efficiency of a cyclone represents the proportion of particles that the cyclone can retain :
Efficiency = (inlet_loading -
outlet_loading)/inlet_loading*100
with :
Efficiency = the efficiency of the cyclone (%)
inlet_loading = the concentration of solids in the gas entering
the cyclone (kg/m3 or grains/ft3)
outlet_loading = the concentration of solids in the gas leaving
the cyclone (kg/m3 or grains / ft3)
2. Calculation of the efficiency of a cyclone : step by step
calculation
2.1 STEP 1 : collect the data
You must gather data on : the cyclone to check, the gas flow, and the solids particles characteristics.
- Cyclone diameter
- Cyclone gas inlet width
- Number of effective turns in the cyclone
- Inlet gas loading in particles
- Particles diameter
- Density of the particles
- Gas inlet temperature
- Gas inlet viscosity
- Gas inlet velocity
2.2 STEP 2 : Cut diameter calculation
The cut diameter is the diameter of particles for which 50% of those particles are collected by the cyclone. Bigger particles will be collected at >50%, smaller particles will be collected at <50%
The cut diameter can be calculated with the following formula [Chopey] :
dpc = [9*μ*Bc/2*π*nt*vi*(ρp-ρ)]0.5
With :
dpc = cut diameter (microns)
μ = gas viscosity (lb/ft.s)
Bc = cyclone inlet width (ft)
nt = number of effective turns in the cyclone (-)
vi = inlet gas velocity (ft/s)
ρp = particle density (lb/ft3)
ρ = gas density (lb/ft3)
2.3 STEP 3 : Calculate the ratio of average particle diameter to the cut diameter
The ratio is equal to :
particle size ratio = dp/dpc
With :
dp = mean particle diameter of the particles in the
inlet flow (microns)
dpc = cut diameter (microns)
Top
5 Most Popular
1.
Pneumatic transport design guide
2. Ribbon
blenders
3. Powder mixing
4. Hoppers design guide
5. Measuring degree of
mixing
--------------
 --------------
--------------
Top 5 New
1. Continuous Dry
Mixing
2. Mixing speed
3. Mixer cycle time
optimization
4.
Batch / continuous mixing comparison
5. Energy Savings
2.4 STEP 4 : Estimate the cyclone efficiency
In order to quickly estimate the cyclone efficiency from the calculations above, the Lapple's curve can be used. This abacus is shown below :
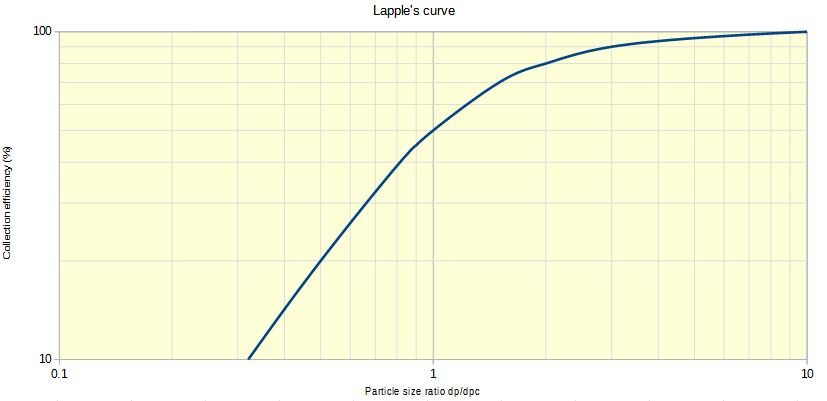
One must use the particle size ratio in order to estimate a cyclone efficiency.
It is also possible to use the following formula [Chopey] :
Efficiency = E = 1/(1+(dpc/dp)2)
With :
E = Efficiency of the cyclone (%)
dp = mean particle diameter of the particles in the
inlet flow (microns)
dpc = cut diameter (microns)
2.5 STEP 5 : Estimate the outlet flow particle loading
Once the efficiency of the cyclone is estimated, it is also possible to estimate the load of the gas flow out of the cyclone.
outlet_loading = inlet_loading*(1-E)
3. Example of cyclone efficiency estimation
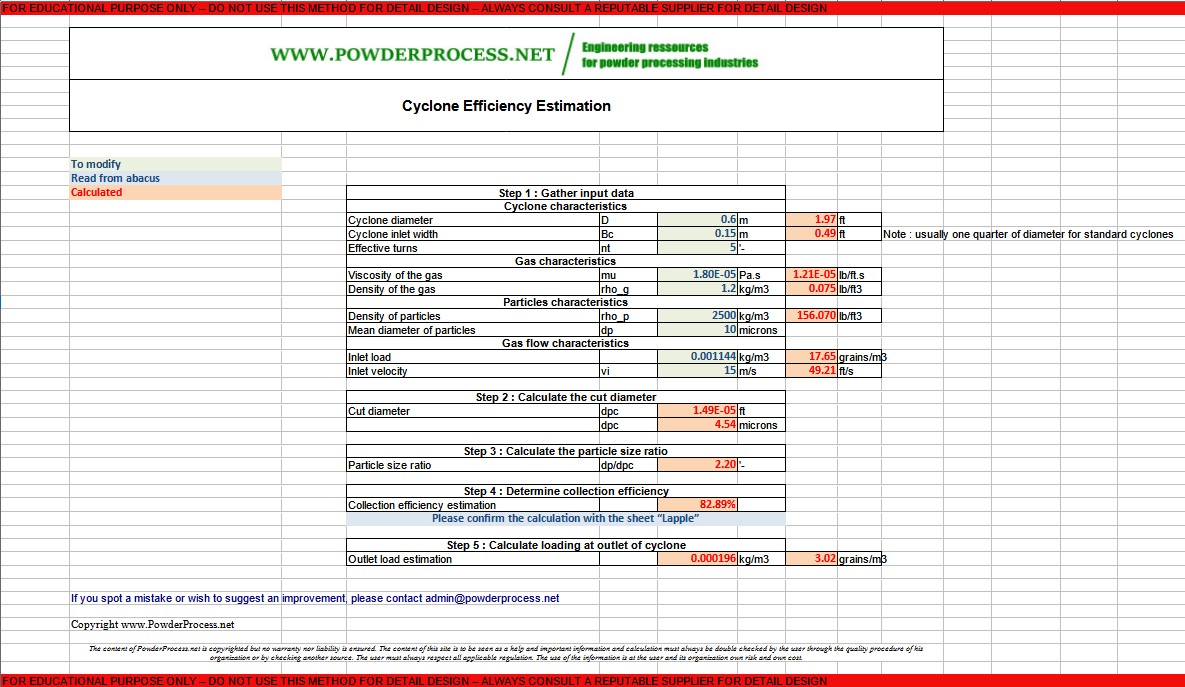
A factory needs to reduce the level of particles emissions out of a particular workshop. A second hand cyclone is available, having a diameter of 0.6 m, an inlet width of 0.15 m and is rated for 5 effective turns. The factory would like to know what will be the efficiency of the cyclone on the workshop air exhaust flow having a load of 17.65 grains / m3, with solids particles of 2500 kg/m3 and mean diameter of 10 microns. On the conditions considered, the inlet velocity of the air flow is 15 m/s and the air viscosity is 1.8*10-5 Pa.s and the air density is 1.2 kg/m3.
3.1 STEP 1 : gather the input data for the calculation
From the data above, one can identify :
μ = gas viscosity (Pa.s) = 1.8*10-5 Pa.s
Bc = cyclone inlet width (m) = 0.15 m
nt = number of effective turns in the cyclone (-) = 5
vi = inlet gas velocity (m/s) = 15 m/s
ρp = particle density (kg/m3) = 2500 kg/m3
ρ = gas density (kg/m3) = 1.2 kg/m3
dp = mean particle diameter of the particles in the inlet flow
(microns) = 10 microns
3.2 STEP 2 : Calculate the cut diameter
The following formula can be used to calculate the cut diameter :
dpc = [9*μ*Bc/2*π*nt*vi*(ρp-ρ)]0.5
However one must note that the inputs must be translated to imperial units.
μ = gas viscosity (Pa.s) = 1.8*10-5 Pa.s = 1.21*10-5 lb/ft.s
Bc = cyclone inlet width (m) = 0.15 m = 0.49 ft
nt = number of effective turns in the cyclone (-) = 5
vi = inlet gas velocity (m/s) = 15 m/s = 49.2 ft/s
ρp = particle density (kg/m3) = 2500 kg/m3 =
156 lb/ft3
ρ = gas density (kg/m3) = 1.2 kg/m3 = 0.075 lb/ft3
dp = mean particle diameter of the particles in the inlet flow
(microns) = 10 microns
dpc = [9*1.21*10-5*0.49/2*π*5*49.2*(156-0.075)]0.5 = 4.54 microns
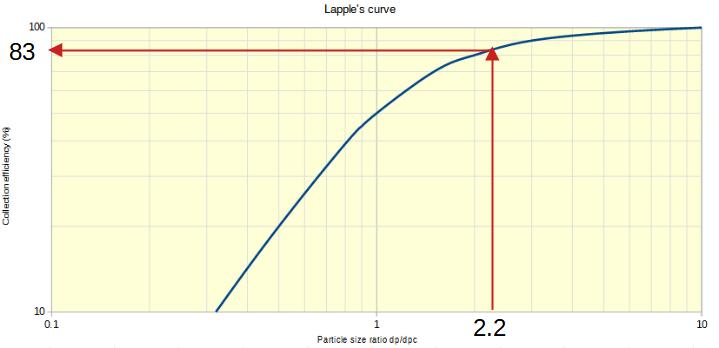
3.3 STEP 3 : Calculate the particle size ratio
The particle size ratio is simply dp/dpc = 2.2
3.4 STEP 4 : Calculate the cyclone collection efficiency estimate
The efficiency can be estimate with the following formula :
Efficiency = E = 1/(1+(dpc/dp)2) = 1/(1+(1/2.2)2) = 0.829
The efficiency is thus estimated for this application at 82.9%
It is always good to double check with Lapple's curve.
3.5 STEP 5 : Estimate the outlet flow particle loading
Thanks to the efficiency of 0.829, the loading of the air flow leaving the cyclone can be calculated as :
outlet_loading = inlet_loading*(1-E) = 17.65*(1-0.829) = 3.02 grains/m3
The cyclone operator can then compare this value to the regulation for example and determine if the cyclone is suitable.
4. Free Excel calculation tool for
estimating a cyclone efficiency
The efficiency of a cyclone based on the calculations shown
above can be estimated thanks to this free Excel calculator : Calculation Tool - Cyclone efficiency
estimation (click here)
Warning : this calculator is provided to illustrate the concepts mentioned in this webpage, it is not intended for detail design. Please consult a reputable designer for all detail design you may need.
 Source
Source
[Chopey] Handbook of Chemical Engineering Calculations, Chopey, MacGraw Hill