
NEWS : Process Engineer's Tools is moving to a new address, www.MyEngineeringTools.com, click here to discover the site |
Reciprocating compressor capacity
| Section summary |
|---|
| 1. Reciprocating compressor capacity calculation formula |
| 2. Usual values |
| 3. Other relations (mass flowrate, power) |
| 4. Multistage compression |
1. Reciprocating compressor capacity calculation formula
In a reciprocating compressor, the capacity depends on the volume displaced by the piston during its movement. The swept volume of one piston can be calculated the following way
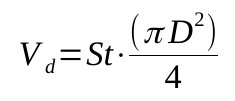
Not all the cylinder volume can be used for the compression as there is always the clearance at the end of the cylinder that remains with some air inside. This phenomena can be quantified by defining the volumetric efficiency of the compressor
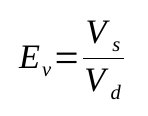
Ev should be calculated rigourously thanks to the actual volume and swept volume, but for quick estimations, the volumetric efficiency can be estimated thanks to the following expression
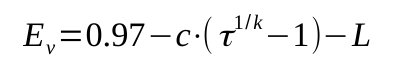
The volumetric capacity of a single piston can then be calculated thanks to
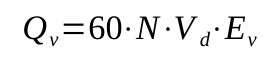
This value needs to be multiplied by the number of cylinders to find out the capacity of the reciprocating compressor.
With
Vd=Swept volume (m3)
Vs=Actual volume capacity (m3)
Vc=Clearance volume (m3)
c=clearance=Vc/Vd=Swept volume (m3)
Ev=volumetric efficiency (-)
τ=compression ration = pdischarge / psuction(-)
St=Piston Stroke (m)
k=isentropic coeffient (-)
D=Cylinder internal diameter (m)
2. Usual values
For air k=1.4
L=0.04 for lubricated compressors (only for estimation)
c must be defined according to the compressor type but should range
from 0.04 to 0.16
3. Other relations (mass flowrate, power)
The mass capacity of the compressor can be calculated, per cylinder with
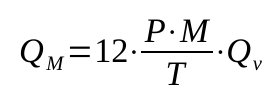

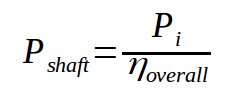

A reciprocating compressor has a cooling system built-in. This particularity, which cannot be implemented for centrifugal compressors, allows to have a discharge temperature close (but not equal) to the isentropic discharge temperature.
4. Multistage compression
Reciprocating compressors are often used in multistage compression with intercoolers in order to maintain the temperatures in a range manageable for the machine. If the compression ratio is > 3, multistage compression is then advised.
