
NFPA 652 Dust Hazard Analysis (DHA) overview, procedure
The Dust Hazard Analysis process within the framework of NFPA 652
Question or remark ? Please contact us at admin@powderprocess.net
| Section summary |
|---|
| 1. What is NFPA
652 ? |
| 2. What is a DHA ? |
| 3. How to do a DHA ? |
| 4. An example of DHA |
This page explains the Dust Hazard Analysis requirements of NFPA 652, especially what is a DHA and how to do a DHA.
1. What is NFPA 652 ?
In US, a standard focusing on combustible dust explosions has been issued by the NFPA : the standard NFPA 652. This standard is mandatory and especially requires the completion of a Dust Hazard Analysis (DHA). The document, as of May 2020, is setting a deadline to complete the DHA by 7th September 2020 and asks for a review and an update every 5 years. Not having completed the DHA properly will result in OSHA citations.
It is similar to European factories that have since 1994 been obliged to comply with a directive called "ATEX" which was aiming at identifying and managing explosion risks in factories. This directive included the gas / vapour explosions which are the ones that were easily thought (although far from always addressed properly) by factory operators of but also included the risks related to the explosion of dust, a hazard much less recognized and that could lead to severe catastrophes (silo explosions typically)
If your company is processing, handling, creating any kind of dust,
then the standard NFPA 652 is applicable and a DHA must be
performed. This does not appear obviously to plant managers but for
example, if you simply have a cutting process generating some dusts
that are aspirated and collected, then a dust explosion risk can
exist and you must run a DHA.
Other relevant standard that derive from NFPA 652 and can be
relevant are the following :
- NFPA 654 – manufacturing, processing, and handling—broadest regulation and the base for the others
- NFPA 61 – agricultural and food processing (organic dusts)
- NFPA 484 – combustible metals
- NFPA 655 – sulfur
- NFPA 664 – wood processing and woodworking
- NFPA 68 – deflagration venting
- NFPA 69 – explosion prevention systems
Factory operators must check which standard is applicable
to their company and apply then.
2. What is a DHA ?
A Dust Hazard Analysis (DHA) is a structured approach to identify, then manage (through prevention or mitigation), the risks associated with dusts at different points of the factory. The Dust Hazard Analysis basically is done in 3 steps :
2.1 STEP 1 Hazard identification : materials combustible
What are and where are the materials combustible or explosible ?
The 1st step of the DHA is to map the production process in order to identify where are potential hazards related to dust fire and / or explosions. It is therefore advisable to perform a DHA with a multidisciplinary team which knows well the working environment and can provide relevant documentation (P&ID, equipment datasheet and drawings...) and which should include a person which has expertise in hazards related to combustible dusts.
The team performing the DHA must then start by gathering explosion data (MIE, MIT, Kst, Pmax...) on the dust handled in the factory, then must be listing the area where combustible dust is present. Once the factory is mapped, the actual hazard must be evaluated.
2.2 STEP 2 Analysis of the hazard
Identify hazards : Does dust hazard really exist ?
Combustible dusts are taking fire and / or exploding in specific conditions. The team carrying out the DHA must then check the following :
- Is there a combustible dust in the area ?
- Can the dust be present in a dust cloud within the Minimum Explosive Concentration ? Or can dust accumulate in layers
- Is there an oxidant (typically oxygen)
- Is there an ignition source ? (if the dust is actually on the form of a deposit, the ignition source can simply be a source of heat)
If the team arrives the conclusion that yes, a combustible powder is in a sufficient concentration / quantity within an oxidant and that a source of ignition can be present, then, there is a hazard, which an be a dust fire or a dust deflagration, and prevention and mitigation actions MUST be taken. The actions will however depend on the level of risk, which can be estimated thanks to a risk assessment matrix.
2.3 STEP 3 Management of the hazard
What are the safeguards to implement ?
There can be many safeguards, but the DHA team must make sure that they apply well to the particular dust hazard considered.
For instance, it can be possible to prevent the explosion by removing one of the elements leading to an explosion :
- Simply avoiding the presence of dust : for example if dust is generated because an equipment is not tight, the replacement of this equipment by a model having a better containment can avoid the risk in the surroundings of the equipment (although probably the risk remain inside)
- Avoiding the presence of the oxidant : Inerting the atmosphere can be a solution to avoid an explosion
- Avoiding the source of ignition : for example, grounding equipment to avoid static electricity sparks, or making sure that a roating part is revolving sufficiently slowly to avoid mechanical sparks
However it is sometimes not possible to prevent reliably an explosion. In this case, the DHA will have to recommend mitigation measures such as explosion panels, suppression systems... etc ... Note that the NFPA standards 68 and 69 may have to be applied during the study.
The conclusions MUST be documented in the DHA and the factory MUST apply the conclusions. It is critical for safety that the risk be properly adressed, an action plan defined and timely executed.

3. How to do a DHA ?
A DHA must be carried out by a multidisciplinary team and must include experts in dust explosion. If the company is large, such expertise can be found within the group, otherwise it is recommended to contact a reputable consultant to support in the process.
Some of the critical concepts required for performing a DHA can be found with the following links
Identification of hazards, material explosion properties
- Characteristics of dust explosion
- Dust explosion concentration
- Dust explosion physical properties
- Dust layer minimum ignition temperature
- Dust
Minimum Ignition Energy MIE
- Dust
Minimum Ignition Temperature MIT
- Dust resistivity
The 1st step of a DHA is to properly collect the different properties of the dust handled. It may be required to carry out specific tests to determine those properties if they are not known or cannot be found in the literature. Defining MIE, MEC, MIT, Kst, Pmax for the ingredients involved is mandatory, other characteristics (resistivity...) may be also required depending on the process.
The plant operator must also gather Pipe & Instrumentation Diagram, layout and equipment characteristics that constitute the production line. Those elements are very important to gauge the risk and define how big are the risk areas in the factory. The documents must be updated so it may require a preparation time to gather and update them prior to starting the DHA.
Analysis of the hazard
- Dust explosion ignition sources
- Electrical equipment
- Electrostatic risks
- Factors influencing dust explosions
- Good housekeeping, avoid secondary explosions
- Mechanical sparks
- Works in dust explosion areas
The identification of hazards should allow to determine where combustible dust can be present in dangerous concentration and at which frequence. The assessment of the risk should then be completed by checking if an ignition source can be located in the area where the dust is present. A risk assessment matrix is recommended to record and classify the different hazards identified during the analysis.
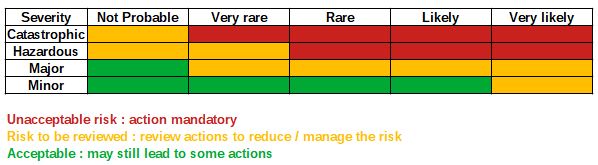
Table 1 : example of DHA risk
analysis matrix
Management of the hazard
Top
5 Most Popular
1.
Pneumatic transport design guide
2. Ribbon
blenders
3. Powder mixing
4. Hoppers design guide
5. Measuring degree of
mixing
--------------
Top 5 New
1. Continuous Dry Mixing
2. Mixing speed
3. Mixer cycle time
optimization
4. Batch
/ continuous mixing comparison
5. Energy Savings
4. An example of DHA
Please follow the link to read an example of DHA
Always remember that Dust Explosion Analysis are mandatory, and conclusions of the risks analysis MUST be implemented by the factory.