
Hopper / silo volume calculation
How to calculate the volume of bulk solids (powder, granules) in a silo ?
Follow us on Twitter ![]()
Question, remark ? Contact us at admin@powderprocess.net
| Section summary |
|---|
| 1. Volume of bulk
solids contained in a hopper or a silo |
| 2. Total volume of
a conical hopper |
| 3. Actual solid
inventory in a silo |
This page is presenting different methods to calculate the total volume of hoppers and the actual volume of bulk solids contained in hoppers, for instance for inventory purpose.
1. Volume of bulk solids contained in a hopper or a silo
When to calculate the volume occupied by solids in a silo or a hopper ?
Solids have a different behavior than liquid when they are poured in a storage vessel : they do not form a flat surface but form a heap, the heap being more or less steep depending on the nature of the solid. As a consequence, there is a strong difference in between the total volume of a hopper (what we could call the "water volume") and the volume that can actually be filled by the solid, what we would call the useful volume.
Such calculations are critical in order to design a new hopper. If one is just using the bulk density of the solids without considering the heap, there are high risks that the vessel will not be large enough. Such calculations are also very useful for existing installation when an engineer wants to check the actual volume of material in a hopper.
Note that the method presented in paragraph 3 below was published years ago, it is approximate but can be already helpful, especially in the 2nd case mentioned above, when someone wants to check the capacity of an existing hopper or know what is the amount of material in an existing hopper.
2. Total volume of a conical hopper
Calculation of the total volume of a conical hopper
Many hoppers and silos are using a conical design. It is the case studied in this page.
Such hoppers are made of :
- A conical bottom
- A cylindrical shell
- A top cover, often elliptical

Conical bottom volume calculation
The volume of a truncated cone can be calculated thanks to the following formula [aqua-calc.com]:
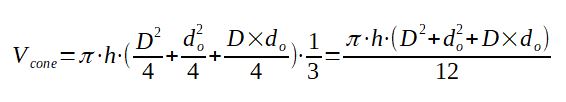
With
Vcone = volume of the conical bottom of the hopper in
m3
D = inside diameter of the shell of the hopper in m
hcone = total height of the conical discharge of the
hopper in m
Do = diameter of the outlet of the hopper in m
Cylindrical shell volume calculation
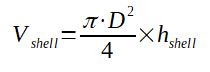
With
Vshell = volume of the cylindrical part of the hopper
in m3
D = inside diameter of the shell of the hopper in m
hshell = total height of the cylindrical part of the
hopper in m
Top cover volume calculation - considering it is an elliptical
cover [webcalc]
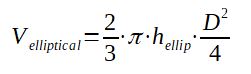
With
Vellip = volume of the elliptical top of the hopper in
m3
D = inside diameter of the shell of the hopper in m
hellip = height of the elliptical cover in m
Note : if the cover of the hopper is not elliptical, please adapt
accordingly.
Top
5 Most Popular
1.
Pneumatic transport design guide
2. Ribbon
blenders
3. Powder mixing
4. Hoppers design guide
5. Measuring degree of
mixing
--------------
 --------------
--------------
Top 5 New
1. Continuous Dry
Mixing
2. Mixing speed
3. Mixer cycle time
optimization
4.
Batch / continuous mixing comparison
5. Energy Savings
3. Actual solid inventory in a silo
How to calculate the actual volume of solids that can be stored in a silo ?
Paragraph 2 allows to calculate the total volume (or water volume) of a hopper, but what about the actual volume of bulk solids contained in this silo ?
The method [Koehler] presented allows to calculate the actual volume of material contained in the heap of product knowing :
- The diameter of the hopper
- The position of the heap (where is the material loaded in the silo)
- The angle of repose of the material

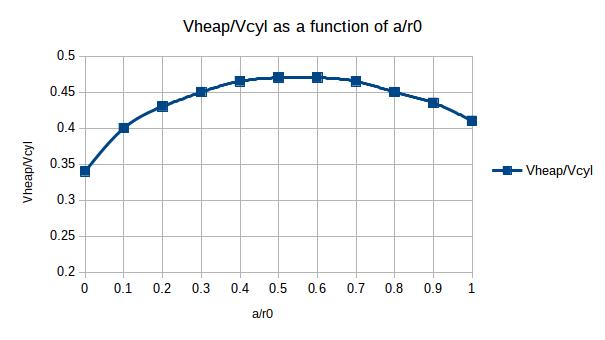
3.1 Calculate the relative position of the heap
The top of the heap is located at a distance a of the center of the silo. The silo has a diameter r0. The ratio a/r0 can then be calculated
3.2 Calculate the height of the heap
This calculation requires to know the angle of repose γ of the material.
The height of the heap b can the be calculated by b = (r0+a).tan(γ)
3.3 Calculation of the volume of the heap
The volume of the heap is equal to Vheap = (Vheap / Vcyl).π.r02.b
With Vheap / Vcyl being determined thanks to the following abacus :
3.4 Calculation of the total volume of solids in the silos
The total volume is then equal to :
Vsolid = Vcone + Vcyl + Vheap
With :
Vcone = the volume of the cone filled by the solid in
m3
Vshell = the volume of the cylindrical shell filled by
the solid in m3, whose height is htotal - b
Vheap = the volume of the heap of solid after loading
in m3
This method is applicable if the cone of the silo is entirely filled and if the method of loading is allowing the formation of the heap of product, which is typically the case when the hopper is loaded by gravity.
3.5 Rough approximation of the maximum volume of solids in a
hopper
Note that at design stage, if an accurate calculation cannot be done, the following approximation can give a 1st idea of what a hopper / silo can really hold in regards to the total volume:
(max volume of product) / (total volume of hopper) = 0.8
It assumes that the formation of the heap of product will lead to a loss of 20% of the total volume of hopper, which cannot actually be filled by product. Again it is only for a very rough estimation at design stage or when troubleshooting an installation.
Source
[Koehler] Estimate the solids inventory in a silo, Frank H. Koehler, Chemical Engineering, 1982
[webcalc] http://www.webcalc.com.br/blog/tank_volume.pdf (page 7, case a = h)
[aqua-calc.com] https://www.aqua-calc.com/calculate/volume-truncated-cone