
Hoppers and silos bulk discharge rates calculation
How to calculate the flowrate of bulk solids unloading from a hopper
Question or remark ? Please contact us at admin@powderprocess.net
| Section summary |
|---|
| 1. Bulk discharge
flow : definitions and calculation methods |
| 2. Hopper
discharge rate calculation : using powder flow
properties measured with shear cells |
| 3. Hopper
discharge rate calculation : using empirical methods |
| 4. Bulk discharge rate Excel
calculation tool |
This page presents different methods found in the literature allowing to perform hopper discharge flow rate calculation and estimate the bulk mass flow rate of powder from an existing bin, or size a new hopper / silo to get a required discharge flow rate.
1. Definition
Process Engineers must often estimate the flow of powder, or more generally bulk solids, that they can get out of a hopper through gravity unloading. Indeed, the calculation of the mass flowrate of particulate solids allows to size the outlet of hoppers or silos, calculate cycle times or make sure that the discharge capacity is enough for the downstream process. However, the calculation of the rate of discharge of a free flow of solids is not easy and depends on many parameters. This page presents different methods found in the literature that can be used to evaluate the discharge rate of powder out of a hopper.

2. Hopper discharge rate calculation method 1 : using shear cells data
In order to estimate the discharge rate of a silo, one of the most reliable method is 1st to have assessed the flowability of the material that will be stored in the hopper. Different methods are available for evaluating the flowability but one of the most reliable, which allows to have quantitative data and not only a relative assessment is to use shear cells. This method requires a lot of testing in order to determine the flow properties of powder but gives the basis for the design of hoppers and the estimation of discharge flow. The method is making the distinction in between coarse and fine powders.
These formulas are reported in the article : Using fundamental powder properties to optimize flowability, Tablets and Capsules, Mehos et al, 2017
Top
5 Most Popular
1.
Pneumatic transport design guide
2. Ribbon
blenders
3. Powder mixing
4. Hoppers design guide
5. Measuring degree of
mixing
--------
Top 5 New
1. Continuous Dry
Mixing
2. Mixing speed
3. Mixer cycle time
optimization
4.
Batch / continuous mixing comparison
5. Energy Savings
2.1 Coarse powder discharge rate
The following formula can be used for assessing the discharge rate of coarse powders :
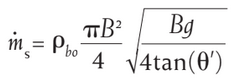
With :
ms = hopper discharge rate in kg/s
B = outlet diameter of the hopper in m
ρbo = powder bulk
density at outlet conditions in kg/m3
θ' =mass
flow hopper angle in deg
2.2 Fine powder discharge rate
Fine powder flow is generally lower than the flow of coarse powder. The fluidization and air balancing - flow of air from downstream to top - being detrimental to the mass flowrate of powder.
The following formula can be used to assess the discharge rate of fine powders.
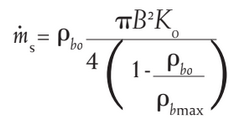
ms = hopper discharge rate in kg/s
B = outlet diameter of the hopper in m
ρbo = powder bulk density at outlet conditions, flowing in kg/m3
ρbmax = powder bulk density at the major consolidation stress in the hopper in kg/m3
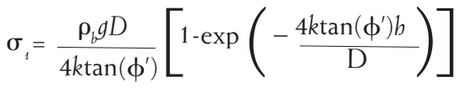
h = depth of powder in the cylinder section in m
k = Janssen coefficient, if unknown can be assumed at 0.4 as 1st approximation
Φ' is the wall friction angle in deg
σ1 = major consolidation stress
3. Hopper discharge rate calculation method 2 : empirical methods
These formulas are reported in the Perry, 8th edition
3.1 Coarse particles (>400 microns)
2 types of equations are usually found in the literature : the Johanson equation and the Berverloo equation. To be noted that these equations will allow to estimate the flow but in no case to have an accurate value.
Beverloo equation is the most direct expression, although different "lump" parameters are used. It is important to note that, for fine particles, the Beverloo equation will overestimate the discharge rate (actually, when discharging fine particles, air fluidization happen which is detrimental to the discharge rate compared to large particles).
Beverloo Equation
![]()
Equation 4 : Beverloo equation (discharge rate through outlet for coarse particles)
W discharge rate in kg/sC empirical discharge coefficient
k empirical shape coefficient
ρb is the bulk density in kg/m3
g is the acceleration of gravity 9.81 m.s-2
dp is the particle diameter in m
d0 is the discharge diameter in m (note for no circular outlet, use hydraulic diameter 4*(cross sectional area)/(outlet perimeter)
C=f(ρb) and is in the range 0.55<C<0.65
k=f(particle shape, hopper angle) and is in the range 1<k<2
except for sand where it is 2.9
If acknown, consider C=0.58 and k=1.6
The Johanson equation has the following form :
Johanson Equation
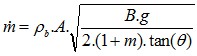
Equation 5 : Johanson equation (discharge rate through outlet for coarse particles)
m_discharge discharge rate in kg/sθ angle of hopper deg
ρb bulk density in kg/m3
g is the acceleration of gravity 9.81 ms-2
Table 1 : Parameters for Johanson equation
| Parameter | Conical hopper | Wedge hopper |
|---|---|---|
| B | D, diameter of outlet | W |
| A | Pi*D^2/4 | WL |
| m | 1 | 0 |
3.2 Fine particles (<400 microns)
As mentionned above, the flow of fine particles will be sensitive to the flow of air returning from the discharge point and opposing the flow of materials. The discharge rate can then be 100 times less than what is predicted by Beverloo or Johanson equations. Carleton proposes an equation to estimate the discharge rate of fine particles.
Carleton Equation
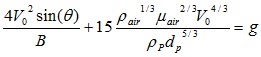
![]()
Equation 6 : Carleton equation (discharge rate through outlet for fine particles)
V0 average velocity of solids dichargingA,B given above
ρp particle density
4. Excel calculation tool : Bulk discharge rate calculator
This calculator allows to estimate the discharge capacity of a hopper, using the formula explained above. It is for information and illustration only, since, as explained in the articles, the formula are giving very approximative results.